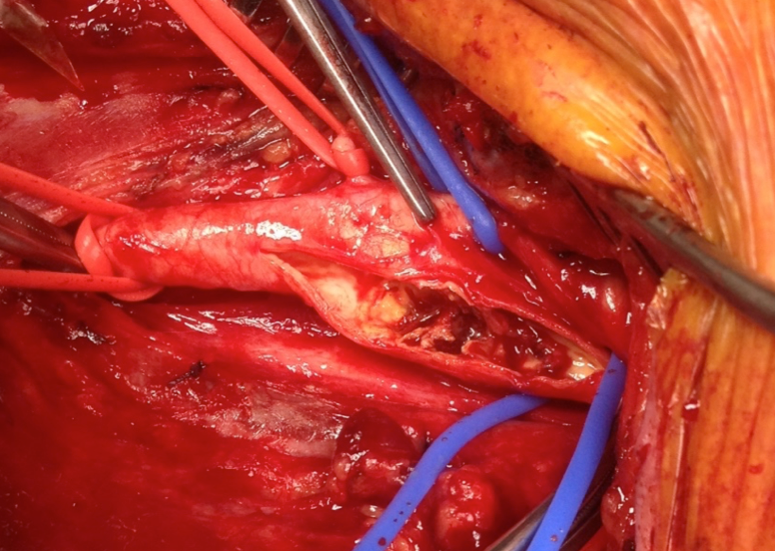
The carotid endarterectomy is the surgical removal of a plaque build up within the carotid artery. The buildup typically occurs where the common carotid artery bifurcates to form the internal and external carotid arteries. Atherosclerosis causes plaque to be deposited along the inside of the artery wall. As plaque builds up in the lumen, blood…(Read More)
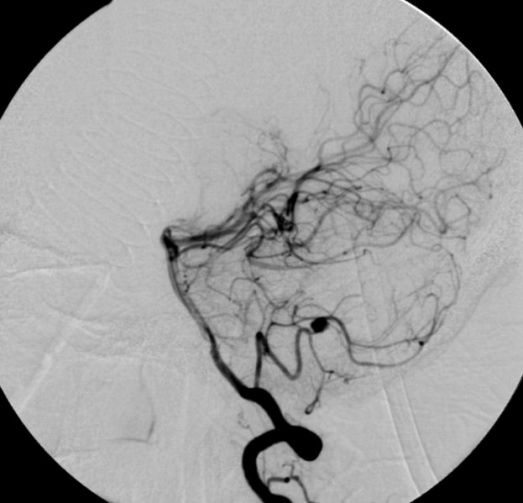
The most common cause of a subarachnoid hemorrhage is the cerebral aneurysm. These can occur along any point of a cerebral artery but there are a number of locations that are most frequent and usually at a branch point. These include the anterior communicating artery, internal carotid/middle cerebral arteries, posterior communicating artery, posterior cerebral…(Read More)
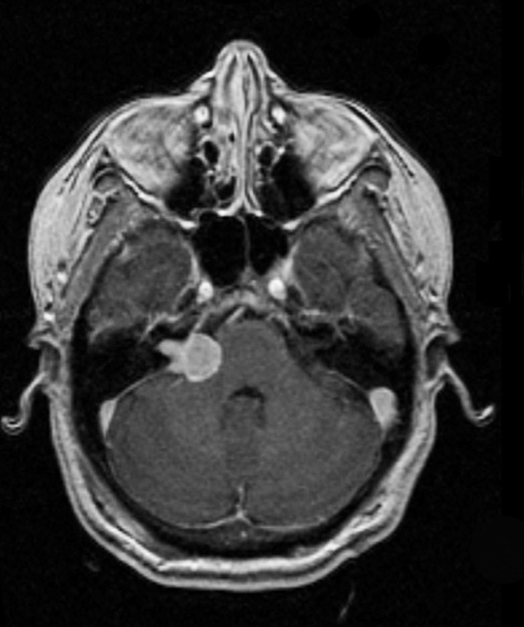
An acoustic neuroma is typically a noncancerous growth on the vestibulocochlear nerve. This is the cranial nerve that connects your inner ear to your brain and is responsible for hearing and balance. If surgical removal of the tumor is indicated, the goal is to preserve the vestibuloocular nerve and the neural structures that receive its…(Read More)
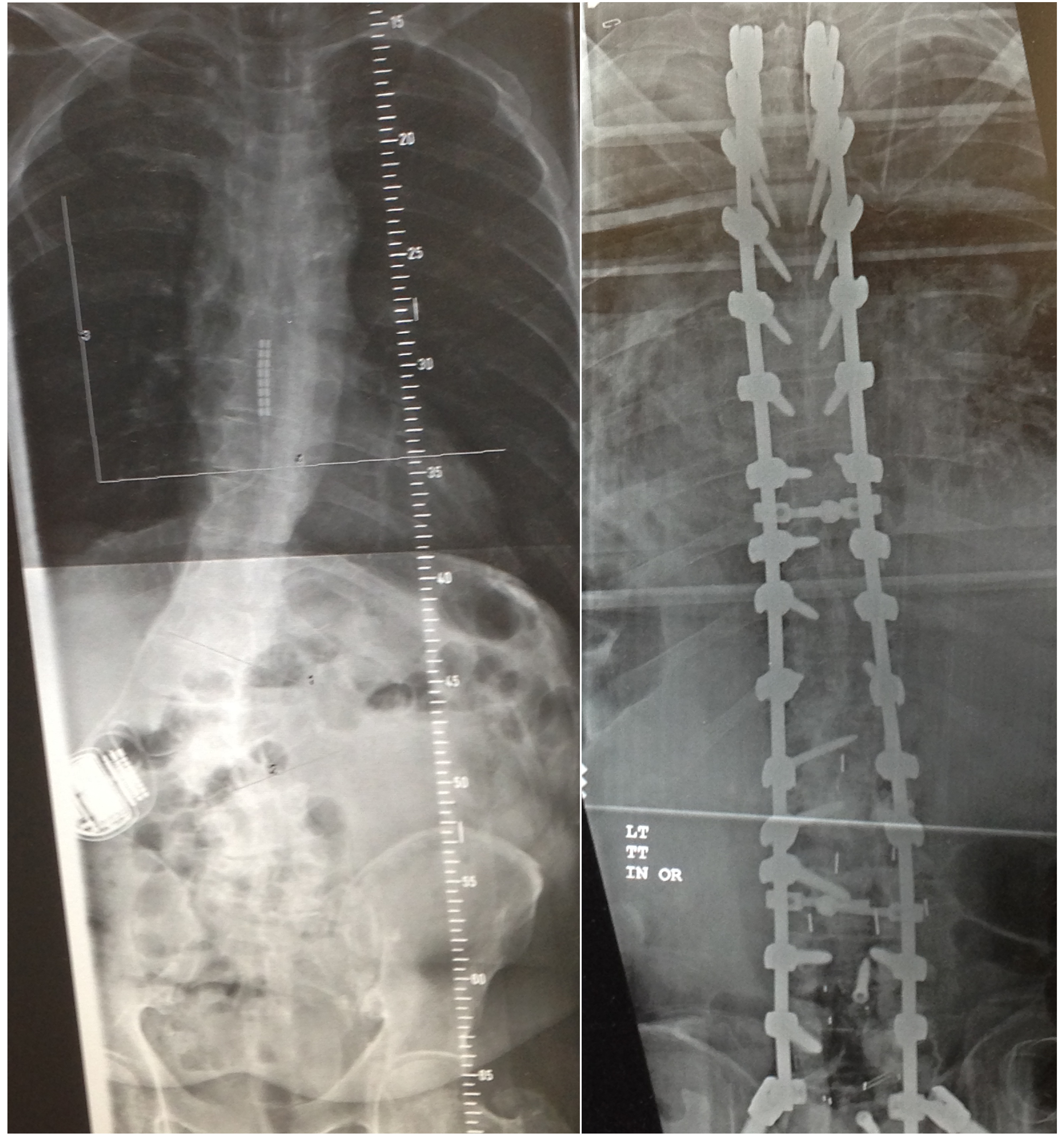
Ideopathic scoliosis is a curvature of the spine. If the curvature is severe enough, a spinal fusion surgery may be indicated. The following link shows an animation of a minimally invasive fusion technique. Why neuromonitoring… During the procedure, the neurophysiologist is continually testing the integrity of the long tracts that travel the length of the…(Read More)
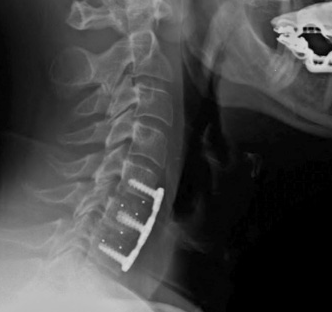
A posterior cervical fusion is performed to stabilize the neck, often this is necessary following a fracture of one or more cervical vertebrae. Why neuromonitoring…  …(Read More)
An ACDF is performed for several reasons, disc herniation or degenerative disc disease is among the most frequent diagnosis. When one or more discs become herniated, they push into the spinal canal and begin compressing the spinal cord (spinal stenosis). A herniated disc can also push to the side and begin compressing the nerve root…(Read More)